Air Conditioners for All-Electric Homes
Air conditioners are air-to-air heat pumps providing cooling and heating directly to the air inside your home.
In winter they use the heat in the outside air, raise the temperature by compressing it then transfer it inside your home. In summer they remove heat from inside your home in a similar way, in reverse.
They are often referred to as reverse cycle air conditioners (RCACs). There are many types on the market today. Find the type that best suits your house design and budget.
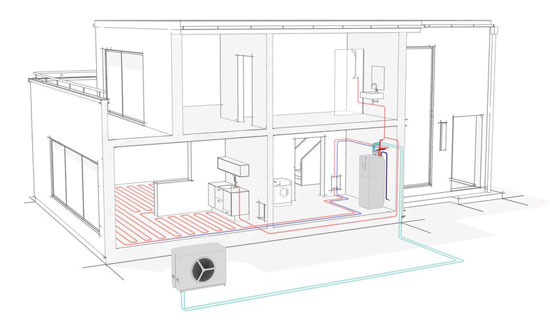
Consider combining your RCAC with air-to-water hydronic heat pumps. This makes a lot of sense because RCACs are better at cooling whilst hydronic heat pumps are better at heating.
RCACs & Hydronic Heat Pumps
Air conditioners provide electric cooling or heating by blowing conditioned air through ducting or from room based indoor units. This is a perfect method for cooling but not the best method for heating.
Air movement alone can make you feel 3 to 4 degrees cooler. However for heating, it is better radiated without air movement. Hydronic air-to-water heat pumps work this way. They use water to transfer heat from an outdoor heat pump to wall mounted radiator panels or though underfloor pipes. These systems then gently radiate heat into your room.
Combined System Placement
For a two storey house, consider radiant hydronic heat pumps on the ground floor, because heat rises. Install RCACs on the first floor, because cool air falls.
For a single storey house, consider RCACs for your bedrooms with hydronic heat pumps for your kitchen and open spaces.
Make sure you have sufficient space to run air conditioning ducting, which will be greater than required for split, multi-split or hydronic systems. Check if this adds costs or constraints to your building design.
Types of Air Conditioners
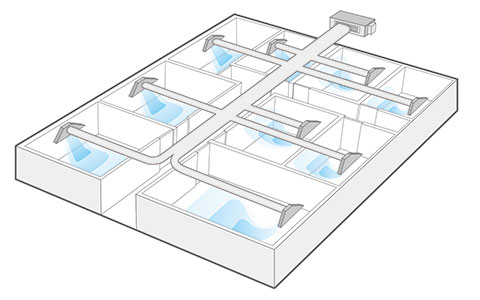
Reverse cycle air conditioners are often ducted systems. This is because they are more cost effective for multiple rooms. Add electronic dampers to zone rooms for individual climate control and lower operating costs.
The key benefits of ducted air conditioning are:
- Control: central space temperature setting with minor room zoning
- Even air distribution: every room has even heating and cooling
- Value: for multiple rooms, it is cheaper to install ducted air conditioning than wall hung split systems
- Aesthetics: the only intrusion to the room is a flush mounted vent that blends with the ceiling
The main downsides are:
- Space, although a roof attic or subfloor may address this issue
- Heat loss or gain through the ducting is greater than with insulated refrigeration or water lines
Other Types
Explore the other types of RCACs available on the market. There is a large range of indoor units available.
Some indoor units are wall mounted. Concealed indoor units can be installed above robes or cabinets, or in drop ceilings.
Cassette types are mounted in ceilings. Small units blow air in 1 direction. Large units blow air in 4 directions.
More Information
Click on the links below for other types of air conditioners or advice about the best system for your project:
